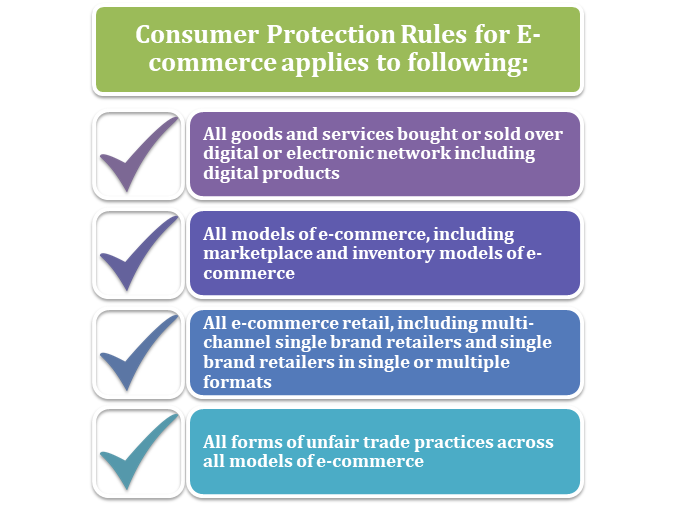
The Central Government, by way of a notification, now makes the consumer protection rules, in the exercise of the powers conferred under section 101, sub-clause (zg) of sub-section (1) of the Consumer Protection Act, 2019. These rules must not apply to any activity of a natural person carried out in a personal capacity, not being part of any professional or commercial activity undertaken on a regular or systematic basis. These rules must apply to an e-commerce entity which is not established in India, but systematically offers goods or services to consumers in India. Also, these consumer protection rules will apply to the following:

Duties of E-commerce Entities
According to Consumer Protection Rules, an e-commerce entity is:
- A company registration under the Companies Act, 2013[1] or a foreign company covered under clause (42) of section 2 of the Companies Act, 2013
- Or an office, branch or agency outside India owned or controlled by a person resident in India provided under section 2 sub-clause (iii) of clause (v) of the Foreign Exchange Management Act, 1999
- Every e-commerce entity must provide the following information in a clear and accessible manner on its platform, displayed prominently to its users, that is:
- The legal name of an e-commerce entity
- The principal address of its headquarters and all branches
- Name and other details of its website
- Contact details like e-mail address, fax, mobile, and landline numbers of customer care.
2. The e-commerce entity must not adopt any unfair trade practice in business on this platform or otherwise.
3. The e-commerce entity must establish an adequate grievance redressal mechanism regarding the number of grievances ordinarily received by such entity from India. It must appoint a grievance officer for consumer grievance redressal to display the name, contact details, and also the designation of such an officer.
4. The e-commerce entity must ensure that the grievance officer acknowledges the receipt of any consumer complaint within 48 hours and redresses the complaint within one month from the date of receipt of the complaint.
5. The e-commerce entity offers imported goods or services for sale. It must provide the name and details of the importer from whom it has purchased such goods or services, or who may be a seller on its platform.
6. The e-commerce entity must endeavor on a best effort basis to become a partner in the process of the National Consumer Helpline of the Central Government.
7. The e-commerce entity must not impose cancellation charges on consumers canceling after confirming purchase unless the e-commerce entity bears similar charges if they cancel the purchase order unilaterally.
8. The e-commerce entity must only record the consent of a consumer for the purchase of any good or service offered, where such consent is expressed through an explicit and affirmative action.
9. The e-commerce entity must accept all payments towards accepted refund requests of the consumers as prescribed by the Reserve Bank of India or any other competent authority under any law for the time being in force, within a reasonable period of time, or as prescribed applicable laws.
10. According to consumer protection rules, the e-commerce entity must not:
- Manipulate with the price of the goods or services offered in such a manner as to gain unreasonable profit by imposing on consumers any unjustified price having regard to the prevailing market conditions, or;
- Discriminate between the same class of consumers or make any arbitrary classification of consumers affecting their rights under the Act.
Liabilities of marketplace E-commerce Entities
- The marketplace e-commerce entity which seeks to avail the exemption from the liability under sub-section (1) of section 79 of the Information Technology Act, 2000 has to comply with sub-sections (2) and (3) of the section, including the provisions under Information Technology (Intermediary Guidelines) Rules, 2011.
- The marketplace e-commerce entity must require sellers through an undertaking to ensure the descriptions, images, and other content pertaining to goods or services is accurate.
- The marketplace e-commerce entity has to provide the following information in a clear and accessible manner, to its users at the appropriate place:
- Details regarding the sellers offering goods and services, including the name of the business, have to mention whether it is registered or not, address, customer care number, any rating or other aggregated feedback about such seller, and any additional information necessary for enabling consumers to make informed decisions at the pre-purchase stage.
- A ticket number for each consumer complaint lodged by which the consumer can track the status of a complaint
- The information relating to return, refund, exchange, warranty and guarantee, delivery and shipment, modes of payment, and grievance redressal mechanism, which is required by consumers
- The information on available payment methods, the security of those payment methods, fees, or charges payable by users, the procedure to cancel regular payments under those methods, charge-back options, and the contact information of the relevant payment service provider.
- All information provided by the sellers under sub-rule (5) of rule 6 and an explanation of the main parameters, which, individually or collectively, are most significant in determining the ranking of goods.
- The marketplace e-commerce entity must include in its terms and conditions generally governing its relationship with sellers on its platform, a description of any differentiated treatment it gives or might give between goods or services or sellers of the same category.
- The marketplace e-commerce entity must make reasonable efforts to maintain a record of relevant information allowing for the identification of all sellers who have repeatedly offered goods or services that have previously been removed or access to which has already been disabled under the Copyright Act, 1957, the Trade Marks Act, 1999 or the Information Technology Act, 2000.
Read our article: How do you file a Complaint against Food Adulteration?
Duties of Sellers at the Marketplace
- The seller offering goods or services through a marketplace e-commerce entity must not adopt any unfair trade practice in the offer on the e-commerce entity’s platform.
- The seller must not falsely represent itself as a consumer and post reviews about goods or services.
- The seller offering goods or services through a marketplace e-commerce entity must not refuse to take back goods, or withdraw or discontinue services purchased or agreed to be purchased, or refuse to refund consideration if paid, if such goods or services are defective, deficient or spurious, or delivered late from the stated delivery schedule.
- The seller offering goods or services through a marketplace e-commerce entity must:
- It must have a prior written contract with respect to the e-commerce entity to undertake or solicit the sale or offer;
- It must appoint a grievance officer for the purpose of consumer grievance redressal and ensure that the grievance officer acknowledges the receipt of any consumer complaint within 48 hours and redresses the complaint within 1 month from the date of receipt of the complaint;
- It must ensure that the advertisements for the marketing of goods or services are consistent with the actual characteristics, access, and usage conditions of such goods or services.
- It has to provide the e-commerce entity its legal name, address of its headquarters and all branches, the name and details of its website, its e-mail address, customer care contact details such as fax, landline, and mobile numbers and also its GSTIN and PAN details.
- The seller offering goods or services through a marketplace e-commerce entity must provide the following information to the e-commerce entity to be displayed on its platform or website:
- The contractual information required to be disclosed by law;
- The total price in the single figure of any good or service, along with the breakup price for the goods or services. It has to show all the compulsory and voluntary charges such as delivery charges, postage and handling charges, conveyance charges, and the applicable tax.
- The mandatory notices and information provided by applicable laws, and the expiry date of the good being offered for sale.
- The relevant details about the goods and services offered for sale by the seller including country of origin which are necessary
- The name and contact numbers, and also the designation of the grievance officer for consumer grievance redressal
- The name and details of the importer, and guarantees related to the authenticity or genuineness of the imported products;
- The accurate information related to terms of exchange, returns, and refund
- The relevant details related to delivery and shipment of such goods or services;
- The relevant guarantees or warranties are applicable to such goods or services.
Duties and Liabilities of Inventory E-commerce Entities
- The inventory e-commerce entity must provide the following information inaccessible manner, displayed prominently to its users:
- The accurate information related to return, refund, exchange, warranty and guarantee, delivery and shipment, cost of return shipping, mode of payments, and grievance redressal mechanism, required by consumers to make informed decisions;
- The mandatory notices and information required by applicable laws;
- The information on available payment methods, the security of those payment methods, the procedure to cancel regular payments under those methods, any fees or charges payable by users
- The contractual information required to be disclosed by law;
- The total price in the single figure of any good or service along with the breakup price for the good or service, showing all the compulsory and voluntary charges, such as delivery charges, postage and handling charges, conveyance charges and the applicable tax.
- The inventory e-commerce entity must ensure that the advertisements for the marketing of goods or services are consistent with the actual characteristics, access, and usage conditions of such goods or services.
- The inventory e-commerce entity must not falsely represent itself as a consumer and post reviews about goods and services or misrepresent the quality of any goods or services.
- The inventory e-commerce entity must not refuse to take back goods, or withdraw or discontinue services purchased or agreed to be purchased, or refuse to refund consideration if paid, if such goods or services are defective, deficient spurious, or if the goods or services are not of the characteristics or features as advertised or as agreed to, or if such goods or services are delivered late from the stated delivery schedule.
- Any inventory e-commerce entity that explicitly or implicitly vouches for the authenticity of the goods or services sold by it, or guarantees that such goods or services are authentic, must bear appropriate liability in any action related to such good or service.
Conclusion
With an increase in online business, there is a requirement to regulate the frauds against the consumers. The Consumer Protection Rules 2020 are made for an e-commerce activity that offers goods and services in India. The provisions under the Consumer Protection Act, 2019, will be applied in case of any violation of the provisions given under consumer protection rules. The Corpbiz Group has a specific knowledge about consumer protection laws. We have professionals that further help our clients in dealing with Consumer Complaints.
Read our article:Here are the Steps to File a Consumer Complaint in India











