India became the second-largest producer & consumer of cement in the world. The rapid expansion of the industrial sector results in a development in construction and infrastructure, and the cement sector is expected to benefit from it vastly. No wonder India’s cement industry is vital to its economy, providing employment to more than a million people directly or indirectly. In some of the recent major government initiatives taken in October 2021, Prime Minister, Mr Narendra Modi, launched the ‘PM Gati Shakti National Master Plan (NMP)’ for multimodal connectivity and created an excellent, seamless multimodal transport network in India. With the increasing demand for cement in the future, the demand for this industry is bound to rise and will attract strict scrutiny from governmental agencies. The project proponent must evaluate the impacts on proposed or existing projects that cause environmental pollution through Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) Reporting by following the legalities of Environmental Clearance for Cement Plants.
Requirement of Prior EC for Cement plants
In some industrial projects, information on the production process, equipment, estimated pollution load, and planned mitigation measures are mentioned in the environmental clearance granted by the concerned authority. The requirement of prior Environmental Clearance for Cement plants which is listed as 3(b) in the schedule as per EIA Notification, 2006, defines the categorization for the project based on the production capacity and grinding units falling under:
- Category A ( MoEF&CC and EAC): ≥ 1.0 Million Tonnes/annum production capacity
- Category B (SEIAA and SEAC): <1.0 Million Tonnes/annum production capacity, All stand-alone grinding units
Table 1.1: List of the Project in Schedule I as Per EIA Notification, 2006 (Amended Notification on 23.11.2016)
| S.No. | Category A | Category B | General Conditions |
| 3(b) | ≥ 1.0 Million Tonnes/annum production capacity | <1.0 Million Tonnes/annum production capacity. All stand-alone grinding units | Fuel for the cement industry may be coal, pet coke, mixture of coal and pet coke and co-processing of waste, provided it meets the emission standards.The manufacturing of composite cement by having environmental clearance for cement plants for the manufacturing of Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC) and Portland Pozzolana Cement (PPC) and Portland Slag Cement (PSC) shall be exempt provided the production is within sanctioned capacity.” |
Before starting any project, preparation of land except for securing the land is stated on the project or activity such as:
- All new projects
- Expansion and modernization of the existing project
- Any change in product mix in an existing manufacturing plant/unit
Process for Obtaining Environment Clearance
The process of obtaining environmental clearance for cement plants consists of the following stages are as follows:
- Screening
- Scoping
- Public consultation, including the process of conduct of Public Hearing
- Appraisal
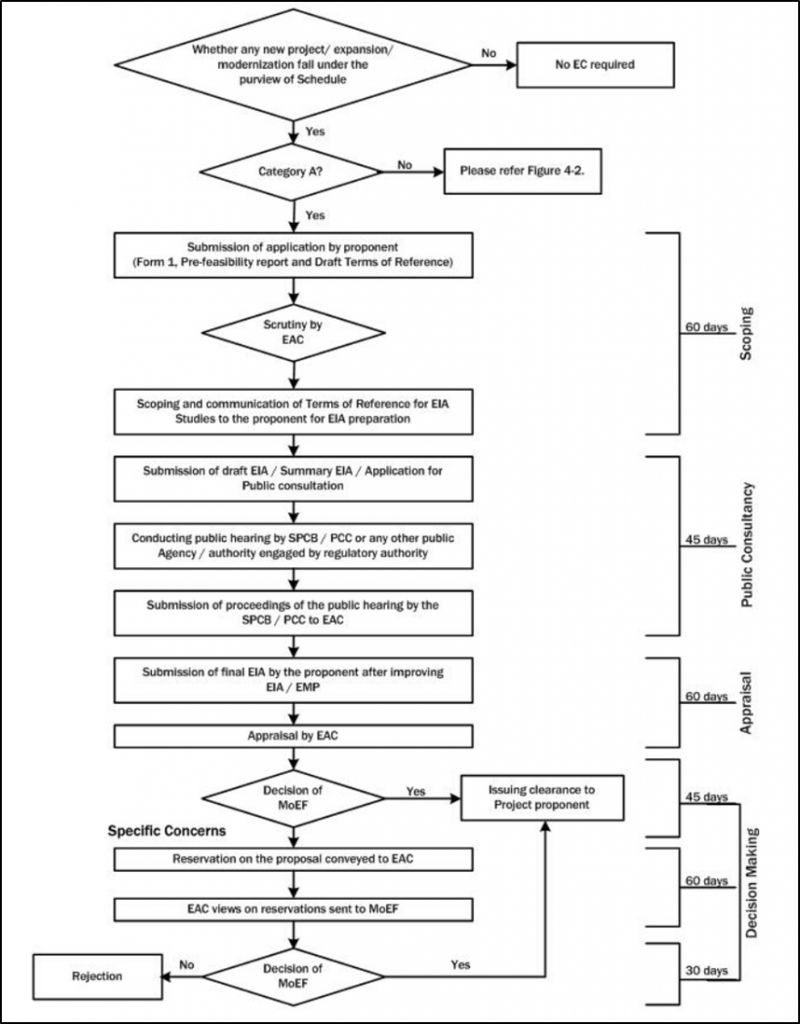

Figure 1.1: Prior Environmental Clearance Process For Category a Projects
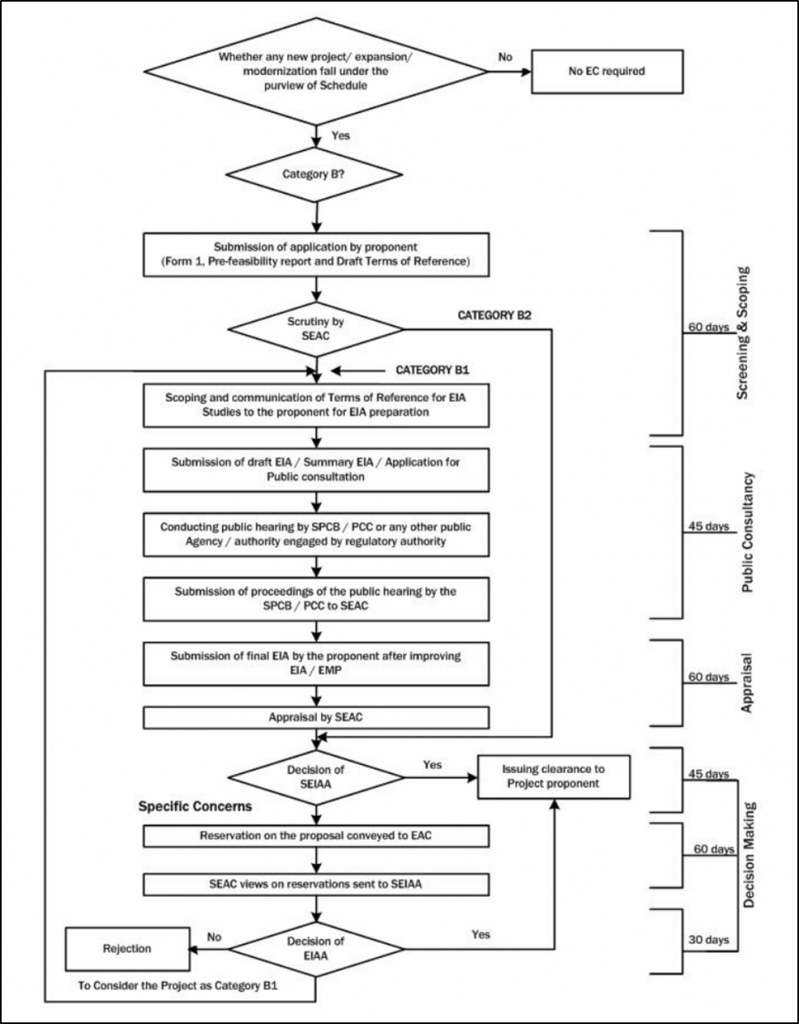

Figure 1.2: Prior Environmental Clearance Process for Category B Projects
Steps in the EIA Process for Environmental Clearance
- Identification of Site Selection by the Project Proponent
- Carrying out a pre-feasibility study required for the prior environmental clearance for cement plants using Form 1 given in Annexure IV of EIA Notification 2006.
- The project proponent has to submit the filled-in Form 1 along with the pre-feasibility report and draft ToR (for Cement Plants) for EIA studies to the concerned authority (through Parivesh portal), i.e., MoEF&CC, Government of India for Category A projects and the SEIAA in case of Category B projects.
- After scrutinizing the documents, the concerned authority declares the results on the portal, whether the project is approved or not. If the project requires an EIA study, the committee releases a ToR letter to the proponent.
- Draft EIA will be submitted in hard copy to SPCB, Zila Parishad, Collector etc., with the incorporation of ToR points required for Public consultation.
- After incorporating the Public hearing minutes in the final EIA report, the project proponent has to submit the required documents (i.e. ToR letter, Final EIA Report, Form-2 etc.) with the help of a consultant on the portal with the same credentials.
- Appraisal and clearance by the concerned authority (i.e. EC letter issued either in hard/soft copy)
Laws and Regulations Applicable For Environment Clearance
Various laws and regulations applicable at the stage of environmental clearance are as follows:
- The Environmental (Protection) Act, 1986, amended 1991
- EIA Notification, 2006[1]
- Forest Clearance as per Forest (Conservation) Act 1980
- Wildlife Clearance (NBWL) as per Wildlife (Protection) Act 1972
- CRZ (Coastal Regulation Zone) Rules.
- Hazardous Waste Management Rules
- Public Liability Insurance Rules, 1991 amended 1993
- Water Act, 1974 amended 1988
Generic Structure of EIA Report
The generic Structure of the EIA report, as mentioned in Appendix III of the EIA Notification, applicable to Cement plants, is designed as per the given layout.
- Introduction
- Project Description
- Description of the Environment
- Anticipated Environmental Impacts & Mitigation Measures
- Analysis of Alternatives (Technology & Site)
- Environmental Monitoring Program
- Additional Studies
- Project Benefits
- Environmental Cost Benefit Analysis
- Environment Management Plan
- Summary & Conclusion
- Disclosure Of Consultants Engaged
Annexures of EIA Report for Obtaining EC
- Land Documents: Land agreement/Lease deed etc.
- Site Photographs: Geotagged site photographs of North, South, East & West directions.
- Primary Data: Baseline Monitoring reports with photographs of Air, Water, Noise & Soil quality of 3 months.
- Secondary Data: Hourly Meteorological by IMD, Climatological, etc.
- Authenticated List of Flora & Faunal species of the study area by DFO.
- DCF certificate showing the availability/non-availability of a National park, Wildlife Sanctuary, Biosphere Reserve, Protected Forest, Elephant corridor/reserve, and Eco-sensitive zone within a 10 Km study area.
- Maps showing topography, geology, land classification, groundwater fluctuation, etc.
- ToR Letter & ToR compliance
- Public Hearing proceedings
- Hydrogeological Report
- CGWA NOC (if applicable)
- Permission from the concerned department showing power and water supply connections.
- Detailed Project Report
- Quality test certificate for analysis of Limestone and slag etc.
- Socio-economic data
- NABET Certificate of Accredited consultant
Composition of the EIA Team
To assess the significant impacts (direct, indirect, and cumulative impacts), the EIA study primarily depends on the constitution of the right team at the right time, preferably at the initial stage of obtaining Environmental clearance for cement plants. The professional team identified for a specific study comprised qualified and experienced professionals from various sectors to address the critical aspects identified in the particular project. Based on nature and the environmental setting, the following professionals may be identified for EIA studies:
- ̇ Environmental management specialist/Regulator
- Cement technologist
- Air and noise quality
- Occupational health
- Geology/geo-hydrology
- Ecologist
- Transportation Specialist
- Safety and health specialist
- Social scientist, etc.
Conclusion
The growing concern of environmental risk in industrial projects such as cement plants and other sectors requires an Environmental clearance to know the production process information, details of energy-efficient equipment, estimated pollution load, and planned mitigation measures. However, to obtain Environmental clearance, a strong EIA practice requires a technical understanding of relevant issues and the measures that work in such circumstances with the guidance of environmental professionals.
Also Read:
How To Proceed For EIA For The Integrated Paint Industry
Overview Of Environment Impact Assessment (EIA) For Industrial Estates
Legalities Involved In Starting A Building And Construction Project











