The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has mandated that all Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs) must file their returns in eXtensible Business Reporting Language (XBRL) format. This requirement was implemented during the financial year 2019-2020.
XBRL is a language designed specifically for electronic communication of financial data between businesses, analysts, investors, regulators, and other stakeholders. It employs a system of unique electronic tags to identify and categorize individual financial terms and information.
The primary objective behind the adoption of XBRL is to streamline the exchange of financial data and minimize the risks associated with misused, misplaced, or mistreated information. By leveraging technology, XBRL enables computers to efficiently track, process, organize, and share financial data in a standardized and structured manner.
XBRL is a part of the broader XML (eXtensible Markup Language) family of languages, which have become the standard for communicating information between businesses and over the internet.
The implementation of XBRL by the RBI aims to enhance the accuracy, transparency, and efficiency of financial reporting by NBFCs, ultimately benefiting all stakeholders involved in the financial ecosystem. This means your financial reporting will be more accurate, transparent, and efficient, leading to a more robust financial ecosystem.
Who Should Make Use of XBRL Filing?
As per the RBI’s guidelines, the NBFCs are required to mandatorily adopt XBRL as their sole return reporting system: The NBFCs are the ones that need to function under XBRL as their exclusive return reporting tool as per the RBI’s specifications. Thus, the micro NBFCs that include the NBFCs whose total assets do not exceed a certain amount of money, which is Rs 500 crores in the present case.
Such NBFCs are required to get themselves registered at the specific XBRL site, and while doing so, it has to provide details of the company, details of KMPs & their contact details as prescribed under the guidelines of the Reserve Bank. The e-mail address that is used in the application for the User ID is the official mode of communication b/w the NBFCs & the Department of Non-Banking Supervision. This means that the flow of financial reporting becomes efficient and, most importantly, unvaried and assists in increasing corporate transparency besides enhancing the ability of the government to supervise the operations of the firms.
Thus, the aforementioned NBFCs have to meet the RBI directive regarding the filing of documents in XBRL to be in regulatory compliance and facilitate information exchange in the financial system.
Points to keep in mind regarding XBRL Return for NBFC
Given below are the significant points to note down pertaining to XBRL Return for NBFC-
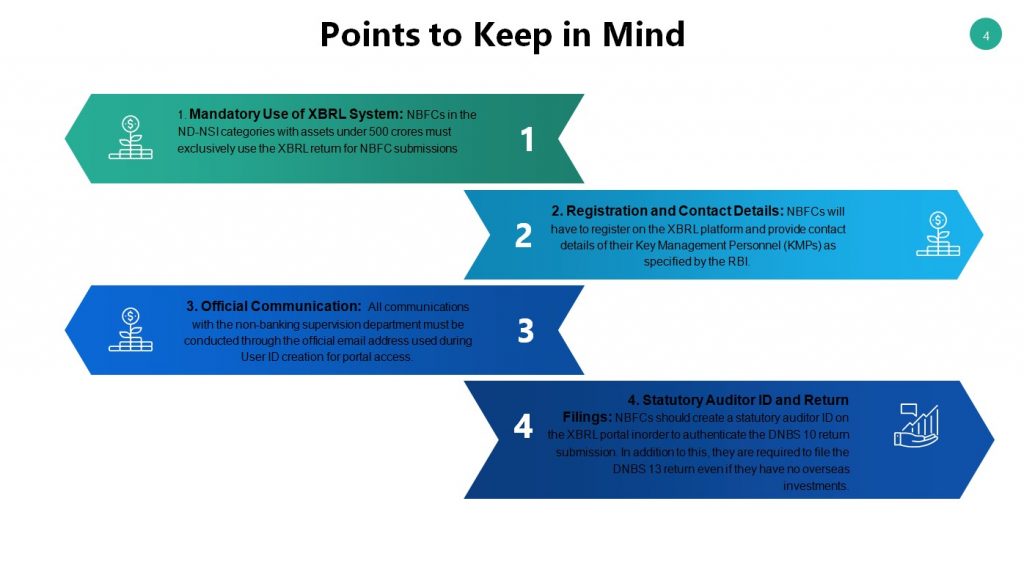

- Mandatory Use of XBRL System:
NBFCs in the ND-NSI categories with assets under 500 crores must exclusively use the XBRL return for NBFC submissions.
- Registration and Contact Details:
NBFCs will have to register on the XBRL platform and provide contact details of their Key Management Personnel (KMPs) as specified by the RBI.
- Official Communication:
All communications with the non-banking supervision department must be conducted through the official email address used during User ID creation for portal access.
- Statutory Auditor ID and Return Filings:
NBFCs should create a statutory auditor ID on the XBRL portal in order to authenticate the DNBS 10 return submission. In addition to this, they are required to file the DNBS 13 return even if they have no overseas investments.
Advantages of XBRL Reporting
The filing of returns through XBRL has its own profitability for Non-Banking Financial companies. Let’s explore some of the key benefits:
- Enhanced Data Analysis: XBRL return for NBFC enables better analysis of the data because the financial data is presented and formatted in standardized machine tags and languages, which also helps in efficient processing.
- Streamlined Data Tracking: The use of XBRL return for NBFC simplifies the tracking and management of financial data, providing a comprehensive overview and ensuring accuracy.
- Qualitative Insights: By leveraging XBRL return, NBFCs can gain access to more in-depth qualitative insights, enabling informed decision-making processes.
- Advanced Decision Support: The structured and standardized nature of XBRL data empowers NBFCs with advanced analytical capabilities, supporting more informed and strategic decision-making.
NBFCs are advised to march ahead with registering themselves on the XBRL platform.
Filing Returns Based on Asset Size for NBFCs
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has prescribed specific returns that Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs) must file, depending on their asset size.
Asset Size Below Rs. 100 Crores
DNBS 02: NBFCs accepting deposits will have to file this return on a quarterly basis, reporting on various financial parameters and indicators. It should be submitted within 15 days after the end of each quarter.
DNBS 10: This form is the statutory auditor’s certificate, which must be filed annually within one month of finalizing the balance sheet. However, it cannot be filed after December 31st.
DNBS 13: These returns will include details about overseas investments (if any) and must be filed within 15 days after the end of each quarter.
If an NBFC has any overseas investments, it is mandatory to file the respective Returns every quarter.
Asset Size Greater than Rs. 100 Crores but Less than Rs. 500 Crores
DNBS 04A: This return focuses on short-term dynamic liquidity and must be filed quarterly within 15 days before the end of the quarter.
DNBS 04B: This return covers structural liquidity and interest rate sensitivity. It needs to be filed monthly, within 10 days before the end of the month.
It’s essential for NBFCs to ensure timely and accurate filing of these returns to maintain regulatory compliance and provide transparent financial reporting to the RBI. Failure to comply may result in penalties or other regulatory actions.
XBRL Instance Documents Creation
To file an XBRL return for NBFC, you must first create the relevant XBRL instance documents.
- Import the tool ‘XBRL Validation Tool’ from the Home page.
- Download the XBRL validation tool from the desired link.
- Upload XBRL instance documents to the validation tool.
- Validate the Instance Documents.
- To review the accuracy and compliance of the instance documents, execute the validation tool.
- Pre-scrutiny of instances Documents.
- Run a Pre-Screener to verify the instance paperwork.
- Convert and verify.
- Change the enabler documents to PDF and double-check the context of the documents.
- Attach to Forms.
- Attach the validated instance documents to Form 23AC-XBRL and Form 23ACA-XBRL.
- Submit on the MCA Portal.
- File Form 23AC-XBRL and Form 23ACA-XBRL on MCA portal.
Stepwise Guide on Filing of XBRL Return for NBFC
The stepwise guidance related to the filing of XBRL Return for NBFC is showcased below in brief-
Step 1: Create the relevant XBRL instance documents
First, start with the company’s financial statements, match each element of the financial statement to the corresponding element in the published taxonomy, create the XBRL instance documents based on the mapped elements, and carefully review and verify the accuracy of the documents.
Step 2: Download the XBRL validation tool from the desired link
The Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA) provides a convenient validation tool on its XBRL portal to help companies ensure the accuracy of their financial statements before filing. It is crucial to validate the instance documents containing the balance sheet and profit & loss account to pinpoint and rectify any discrepancies or errors. Companies can easily obtain this validation tool by downloading it directly from the MCA XBRL website.
Step 3: Upload XBRL instance documents to the validation tool
Click “Open” to load an instance document. To validate additional documents, simply click “Open” again without exiting the tool. Each loaded document’s company details appear under the “General Information” tag in the XBRL viewer. This user-friendly approach streamlines the validation workflow for multiple instance documents.
Step 4: Validate the Documents using the tool
At this step, we need to validate the document properly. To do that, follow these steps:
- Check that the instance document matches the latest and correct version of the taxonomy set by the Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA).
- Make sure all the mandatory items or elements have been filled in.
- Go through the other business rules specified by the MCA and ensure the document follows them.
- Perform any other validations required as per the taxonomy guidelines.
Essentially, we need to carefully validate that the instance document meets all the taxonomy, mandatory elements, business rules, and other requirements laid out by the MCA.
Step 5: Pre-Scrutinizing the Instance Document
After validating the instance documents, the next step is to pre-scrutinize them using the same tool. For pre-scrutinizing, you’ll need an internet connection. During the pre-scrutiny process, you need to check for server-side validations that the MCA21 system does not validate itself.
In simple terms, pre-scrutiny involves checking the instance documents against additional validation rules that are not covered by the MCA21 system’s own validations. This extra layer of scrutiny is done online and requires an internet connection to work.
Step 6: Verification of Documents
After pre-scrutinizing the documents, the next step is to generate a PDF using the ‘Export to PDF’ option in the tool. You’ll then need to verify the final instance documents. If there’s an error while converting to PDF or if the PDF size is zero kilobytes, you will need to check the textual information entered in the instance document.
Follow the HTML guidelines mentioned in the technical specifications to correct any issues in the instance documents. Once corrected, you’ll have to go through the pre-scrutiny process again.
Step 7: Attaching Documents to the Form
The MCA portal provides Form 23AC-XBRL and Form 23ACA-XBRL for filing financial statements in the XBRL format. Filing financial statements on the MCA portal is of utmost importance, so begin by filling out these forms. Then, attach the validated and pre-scrutinized instance documents for the Balance Sheet to Form 23AC-XBRL. Similarly, attach the instance document for the Profit and Loss account to Form 23ACA-XBRL. Then, attach separate instance documents for Standalone and Consolidated financial statements.
Step 8: Submitting the Form
After completing the form, perform a pre-scrutiny, sign the form, and then upload it. Validate the form by confirming that all validation steps have been carried out through the tool.
Step 9: Viewing the Balance Sheet and Profit & Loss Statement
The documents submitted with Form 23AC-XBRL and 23ACA-XBRL are in machine-readable format. To facilitate human readability, these documents must be converted through the MCA21 system. In order to view the converted documents on the MCA portal and obtain certified copies, the availability of these converted documents is imperative.
The Final Words
Adhering to the XBRL return for NBFC filing requirement set forth by the Reserve Bank of India is an important compliance measure for Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs). By adopting the XBRL return for NBFC filing format, NBFCs can streamline their financial reporting processes, enhance data accuracy, and improve transparency. The step-by-step approach abstracted in this guide provides a comprehensive roadmap for NBFCs to helm the XBRL return for the NBFC process seamlessly.
By staying compliant with the XBRL return for NBFC filing mandate, NBFCs can position themselves as forward-thinking entities, committed to upholding industry best practices and contributing to a more robust and transparent financial ecosystem through accurate XBRL return for NBFC filing.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is XBRL, and why is it important for NBFCs?
XBRL stands for eXtensible Business Reporting Language. It is a standardized format for communicating financial data electronically. The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has mandated XBRL Return for NBFCs to enhance transparency, accuracy, and efficiency in financial reporting.
Which NBFCs are required to file XBRL returns?
NBFCs with total assets exceeding Rs. 500 crores are mandated to adopt XBRL as their sole return reporting system. Micro NBFCs with total assets below Rs. 500 crores are also required to file XBRL returns.
What are the key advantages of XBRL return for NBFC filing?
Key advantages include enhanced data analysis, streamlined data tracking, qualitative insights, and advanced decision support due to the structured and standardized nature of XBRL data.
What are the different returns that NBFCs need to file based on their asset size?
NBFCs with assets below Rs. 100 crores need to file DNBS 02, DNBS 10, and DNBS 13 returns. Those with assets between Rs. 100 crores and Rs. 500 crores must file DNBS 04A and DNBS 04B returns.
What is the process for filing XBRL returns?
The process involves creating XBRL instance documents, validating them using the MCA's tool, pre-scrutinizing, generating PDFs, attaching documents to MCA forms (23AC-XBRL and 23ACA-XBRL), submitting the forms, and viewing the converted documents on the MCA portal.
What should NBFCs do if there are errors while converting instance documents to PDF?
If there are errors during PDF conversion or if the PDF size is zero kilobytes, NBFCs should check the textual information in the instance document, follow HTML guidelines to correct issues, and then go through the pre-scrutiny process again.
How often do NBFCs need to file XBRL returns?
The frequency of filing XBRL returns depends on the specific return and the NBFC asset size. For example, DNBS 02 (for deposits) needs to be filed quarterly, DNBS 10 (auditor's certificate) annually, and DNBS 13 (overseas investments) quarterly.
Is it mandatory for NBFCs to create a statutory auditor ID on the XBRL portal?
Yes, NBFCs are required to create a statutory auditor ID on the XBRL portal to authenticate and file the DNBS 10 return submission.
What happens if an NBFC fails to comply with the XBRL filing requirements?
Failure to comply with the XBRL filing mandate may result in penalties or other regulatory actions from the Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
Can NBFCs use any XBRL validation tool?
The Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA) furnishes a convenient XBRL validation tool on its portal, which is recommended for NBFCs to ensure accuracy and compliance before filing their returns.
Read our article Understanding RBI Regulation For NBFC License











