If you want to carry out an environment-friendly business that uses plastic packaging, in that case, EPR Registration is one of the important obligations that need to be fulfilled. A legal framework known as EPR plastic registration has been put in place in many nations to transfer control over the management of the end-of-life disposal of plastic products from consumers and municipalities to those plastics manufacturers. EPR’s main goal is to hold manufacturers operationally and financially responsible for the environmental impact of their plastic products throughout every stage of their lifecycle, from manufacturing to disposal.
Products made of plastic are now a necessary component of our daily lives. It is made in great quantities all over the world. At a rate of about 5.6 million tonnes per year (TPA), plastic waste is produced in India. Its disposal is a main problem. Although recyclable, it’s still important to find alternatives to plastic in its entirety.
The Extended Producers Responsibility (EPR) regime is being implemented in the 2016 Plastic Waste Management Rules to ensure the processing of plastic packaging waste, which states that it is the producers’, importers’, and brand owners’ responsibility to see to it that the plastic packaging waste they generate is recycled, repurposed, or disposed of at the end of its useful life.
Purpose of EPR Plastic Registration
The EPR plastic registration program motivates importers, brand owners, and plastics manufacturers to develop products that are easy to recycle, generate less plastic waste, and have a lesser impact on the environment.
Synopsis of EPR Plastic Registration
Extended Producer Responsibility, or EPR, is a framework that places the producer or manufacturer, not the consumer or local government, in charge of managing a product’s life cycle, including its disposal and recycling. EPR programs can vary from one area or nation to another, but they typically have two main objectives:
- To encourage environmentally friendly product design
- Lessen the negative effects of products, including plastics, on the environment.
EPR registration certificate
The following organizations must apply for an EPR registration certificate through the central EPR portal created by the CPCB:
- Producer
- Importer
- Brand owner
- Plastic Waste Processors have involvement in recycling, waste to energy, waste to oil, and industrial composting, among other activities.
Process for EPR Plastic Registration
EPR Plastic Registration encourages importers, brand owners, and plastics manufacturers to develop products that are easy to recycle, generate less plastic waste, and have a lesser impact on the environment.Depending on where you are, there may be different procedures for EPR plastic registration of plastic products because every country and region may have different rules and regulations. The general outline of the steps in the EPR plastic registration process, though:


- Research and Understand Local Regulations: To begin with, do a thorough investigation of the EPR laws and requirements that apply to your area or nation. Environmental agencies as well as the waste management authorities, or other governmental authorities may be in charge of the management of these regulations.
- Determine Your Obligations: – Determine whether your company is liable for EPR compliance for plastic products as a producer, manufacturer, or importer. Regulations frequently specify which companies must take part in EPR programs.
- Fulfill the Registration Application: – Create and send the necessary registration application forms and supporting materials. – Company information and contact information are frequently among the specific documents and data required.
- Information on the kinds of plastic goods you manufacture, import, or sell.
- Approximations of the market share of plastic products.
- The strategies you have in mind to manage the end-of-life of these products, such as recycling, collection, or disposal plans.
- Financial data about any fees or contributions needed to comply with EPR regulations
- Pay Any Required Fees: – Several EPR programs may ask participants to pay fees or make financial contributions to help fund waste management or recycling initiatives.
- Compliance Reporting: Following registration, you might be asked to submit recurring reports on your EPR activities, which may include information on recycling rates, waste reduction programs, and other pertinent metrics. Keep complete records for reporting requirements.
- Compliance Audits: – Be ready for potential regulatory authority compliance audits to ensure that you are correctly adhering to EPR regulations. Keep clear records and supporting documents to prove your compliance.
- Working together with recycling facilities: Partnerships with authorized recycling facilities or organizations in charge of handling plastic waste are common in EPR programs. Make sure you are collaborating with authorized and compliant partners.
- Environmental Goals: Recognize any environmental objectives or targets related to the EPR program, such as raising recycling rates or lowering plastic waste production.
- Stay Informed and Adapt: EPR guidelines and requirements could change in the future, so staying informed and adapting to new regulations are required.
Analysis of EPR Plastic Waste Management
Different regions and nations implement EPR plastic waste management in different ways, and there can be differences in the precise specifications and rules. It is crucial for consulting the relevant environmental agencies, regulations, and guidelines unique to your jurisdiction to comprehend the specific provisions and procedures of EPR managing plastic waste in your area. Environmental consultants and industry associations can also be helpful in advising on adherence to the requirements of EPR.
EPR plastic waste management is a legal strategy that places producers, manufacturers, and brand owners—rather than consumers or local governments—in charge of managing the entire lifecycle of plastic products. EPR initiatives seek to advance environmentally friendly product development, lessen plastics’ negative environmental effects, and promote recycling and ethical disposal
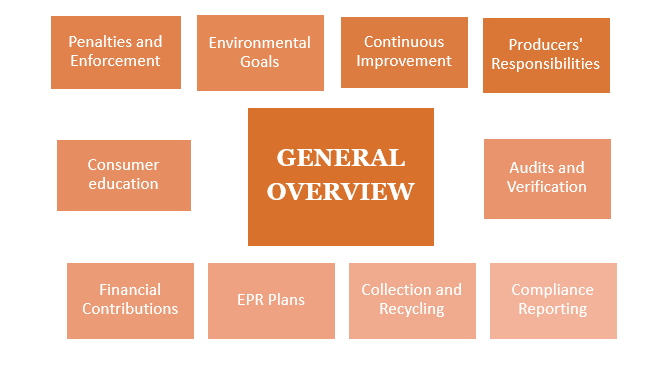

Fig. Element in managing EPR for plastic waste
How to manage EPR plastic waste?
- Producers’ Responsibilities: According to EPR, manufacturers, importers, and brand owners are all required to bear legal responsibility for the plastic waste that their products cause to be produced. This includes different kinds of plastic packaging and goods.
- Collection and Recycling: Producers must put in place systems for the collection, transportation, recycling, and appropriate disposal of plastic waste. To make sure the management of plastic waste is done properly, they might set up collection points or collaborate with recycling facilities.
- EPR Plans: Producers are required to create and submit EPR plans outlining their strategies for handling plastic waste to the appropriate regulatory bodies. These plans go into great detail about waste minimization, recycling, and waste collection methods.
- Financial Contributions: To support initiatives to manage plastic waste, EPR programs frequently ask producers to make financial contributions. The infrastructure for recycling, awareness campaigns, and other waste reduction initiatives could all be built and maintained with the help of these funds.
- Compliance Reporting: Producers are frequently required to submit periodic reports on their plastic waste management activities, which must include information on the quantity of plastic that is gathered, recycled, and properly disposed of.
- Audits and Verification: Regulatory agencies may carry out audits or verifications to make sure producers are adhering to their EPR obligations. It helps in promotion, maintaining accountability and transparency.
- Consumer education: EPR programs frequently incorporate public awareness and education campaigns to inform consumers about appropriate disposal and recycling practices for plastic products.
- Environmental Goals: EPR programs consist of particular environmental objectives, which include boosting recycling rates, cutting down on plastic waste, or lessening the negative effects of plastics on the environment.
- Penalties and Enforcement: The regulatory authorities may impose fines and pursue legal action if EPR regulations are not followed.
- Continuous Improvement: Producers are encouraged to improve their efforts to manage plastic waste, which may include new product designs, a decrease in the use of single-use plastics, and the investigation of sustainable substitutes.
Legality vis-a-vis EPR plastic waste management
The Plastic Waste Management Rules, 2016, which were published by the provisions of the Environment (Protection) Act, 1986[1], set forth Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) regulations about the management of plastic waste in India.
Aim of the Act
To ensure proper management of plastic waste, these regulations needed EPR from plastic manufacturers, brand owners, and importers.
Key points of the Act
- Application: The regulations apply to manufacturers, owners of brands, and importers of plastic goods, including packaging components.
- Responsibilities: The collection, segregation, transportation, recycling, and safe disposal of plastic waste produced as a result of a product’s use are the producers, brand owners, and importers of plastic goods.
- EPR Action Plan: These stakeholders must create an EPR plan outlining their strategies for handling and recycling the plastic waste produced by their goods. The State Pollution Control Boards or Pollution Control Committees should review and approve this plan.
- Registration: To comply with the regulations, producers, brand owners, and importers may need to register with the relevant authorities or organizations in charge of enforcing and monitoring EPR compliance.
- Compliance Reporting: The registered entities are required to submit periodic reports on their EPR activities, which should consist of information on the gathering and recycling of plastic waste.
- Fees and Financial Contributions: The regulations may outline the fees or monetary contributions that registered entities must make to help fund initiatives to manage and recycle plastic waste.
- Audit and Verification: To make sure that registered entities are fulfilling their EPR obligations, the appropriate authorities may carry out compliance audits and verifications.
- Penalties: Violations of the EPR regulations could result in fines or other sanctions as specified by the rules.
Conclusion
A crucial regulatory framework called EPR plastic registration was created to address the environmental problems caused by plastic waste. It is important for combating the issue of global plastic pollution and advancing the circular economy. According to EPR, plastic manufacturers are required to assume financial and operational liability for the collection, recycling, or proper disposal of their products made of plastic. Producers must register with the appropriate agencies, comply with reporting standards, and meet recycling goals. Penalties may apply for non-compliance. In the end, EPR plastic registration encourages manufacturers to use more environmentally friendly practices, reduce plastic waste, and support plastic production and disposal that is less harmful to the environment.
FAQs
The Extended Producers Responsibility (EPR) regime is being implemented in the Plastic Waste Management Rules, 2016. According to this, Producers, importers, and brand owners are responsible for ensuring that their plastic packaging waste is processed through recycling, re-use, or end-of-life disposal.
The following organizations must apply for an EPR registration certificate through the central EPR portal created by the CPCB: • Producer • Importer • Brand owner • Plastic Waste Processors are involved in recycling, waste to energy, waste to oil, and industrial composting, among other activities.
EPR plastic waste management is a legal strategy that places producers, manufacturers, and brand owners—rather than consumers or local governments—in charge of managing the entire lifecycle of plastic products. EPR initiatives seek to advance environmentally friendly product development, lessen plastics’ negative environmental effects, and promote recycling and ethical disposal.
The EPR plastic registration program encourages importers, brand owners, and manufacturers of plastics to create goods that are simpler to recycle, produce less plastic waste, and have a smaller environmental impact.
The Extended Producers Responsibility (EPR) regime is being implemented in the 2016 Plastic Waste Management Rules to ensure the processing of plastic packaging waste which states that it is the producers’, importers’, and brand owners’ responsibility to see to it that the plastic packaging waste they generate is recycled, repurposed, or disposed of at the end of its useful life.
Read Our Article: EPR Plan For Plastic Import In India











